|
5 modules to solve YOUR homework problem with a step-by-step explanation
|
The Thermochemistry module has five sub modules providing problem-solving engines for typical thermochemistry problems.
• Standard Enthalpy of Formation (ΔH f º)
The enthalpy change of a chemical reaction can be calculated using the ΔH f º of the substances (reactants and products) involved in the reactions shown in the following formula:
ΔHº reaction = Σn p ΔH f º(products) - Σn r ΔH f º(reactants)
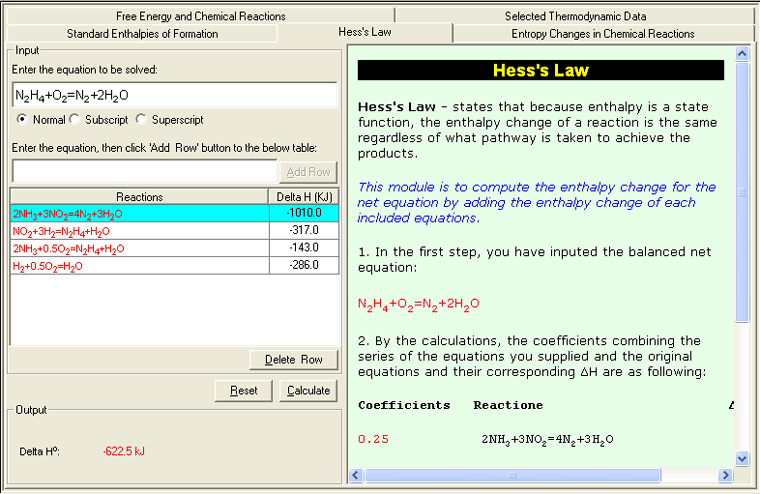
• Hess's Law
Because enthalpy is a state function , the enthalpy change of a reaction is the same regardless of what pathway is taken to achieve the products . In other words, only the start and end states matter to the reaction, not the individual steps between. This module is to compute the enthalpy change for the net equation by adding the enthalpy change of each included equations.
• Entropy (S)
Because entropy is a state function of a system, the entropy change in chemical reactions can be calculated by taking the difference between the standard entropy values of products and those of the reactants:
ΔSº reaction = Σn p Sº(products) - Σn r Sº(reactants)
• Free Energy (G)
Since free energy is a state function. As calculations in enthalpy changes (ΔHº) and entropy changes (ΔSº), the free energy can be calculated by:
ΔGº reaction = Σn p ΔGº(products) - Σn r ΔGº(reactants)
• Thermodynamic Data
The table provides handy reference with list of the Selected Thermodynamic Data . Including ΔH f º, ΔG f º and Sº at standard condition of 25ºC, 1 atm. The entire table of data can be easily printed by right-click on the table. Similarly, you may copy your selected data (cell. Row, or column) and paste it to the input box of a SoftChemistry module or other common document.